Maverick and Comet Repair
Engine Electrical
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
Starting System
The battery is the first link in the chain of mechanisms which work
together to provide cranking of the automobile engine. In most modem
cars, the batten is a lead-acid electrochemical device consisting of
six two-volt (2V) subsections connected in series so the unit is
capable of producing approximately 12 V of electrical pressure. Each
subsection, or cell, consists of a series of positive and negative
plates held a short distance apart in a solution of sulfuric acid
and water. The two types of plates are of dissimilar metals. This
causes a chemical reaction to be set up, and it is this reaction
which produces current flow from the battery when its positive and
negative terminals are connected to an electrical appliance such as
a lamp or motor. The continued transfer of electrons would
eventually convert the sulfuric acid in the electrolyte to water,
and make the two plates identical in chemical composition. As
electrical energy is removed from the battery, its voltage output
tends to drop. Thus, measuring battery voltage and battery
electrolyte composition are two ways of checking the ability of the
unit to supply power. During the starting of the engine, electrical
energy is removed from the battery. However, if the charging circuit
is in good condition and the operating conditions are normal, the
power removed from the battery will be replaced by the alternator
which will force electrons back through the battery, reversing the
normal flow, and restoring the battery to its original chemical
state.
The battery and starting motor are linked by
very heavy electrical cables designed to minimize resistance to the
flow of current. Generally, the major power supply cable that leaves
the battery goes directly to the starter, while other electrical
system needs are supplied by a smaller cable. During starter
operation, power flows from the battery to the starter and is
grounded through the car's frame and the battery's negative ground
strap.
The starting motor is a specially designed, direct current
electric motor capable of producing a very great amount of power for
its size. One thing that allows the motor to produce a great deal of
power is its tremendous rotating speed. It drives the engine through
a tiny pinion gear (attached to the starter's armature), which
drives the very large flywheel ring gear at a greatly reduced speed.
Another factor allowing it to produce so much power is that only
intermittent operation is required of it. Thus, little allowance for
air circulation is required, and the windings can be built into a
very small space.
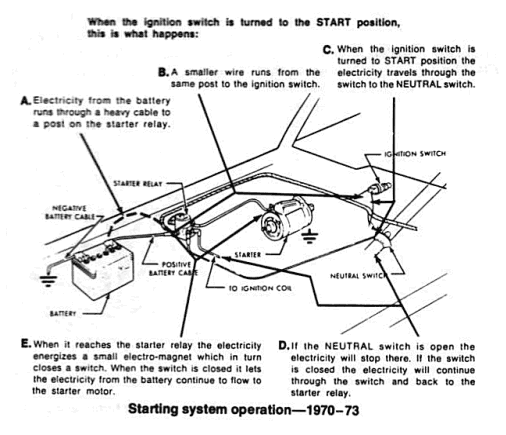
The starter solenoid is a magnetic device which employs the small current supplied by the starting switch circuit of the ignition switch. This magnetic action moves a plunger which mechanically engages the starter.
Ford starters employ a separate relay, mounted away from the starter, to switch the motor and solenoid current on and off. The relay thus replaces the solenoid electrical switch, but does not eliminate the need for a solenoid mounted on the starter used to mechanically engage the starter drive gears. The relay is used to reduce the amount of current the starting switch must carry.
The starting switch circuit consists of the starting switch contained within the ignition switch, a transmission neutral safety switch or clutch pedal switch which prevents the car from being started in any gear but Neutral or Park (automatic only), and the wiring necessary to connect these in series with the starter solenoid or relay.
A pinion, which is a small gear, is mounted to a one-way drive clutch. This clutch is splined to the starter armature shaft. When the ignition switch is moved to the "start" position, the solenoid plunger slides the pinion toward the flywheel ring gear via a collar and spring. If the teeth on the pinion and flywheel match properly, the pinion will engage the flywheel immediately. If the gear teeth butt one another, the spring will be compressed and will force the gears to mesh as soon as the starter turns far enough to allow them to do so. As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its travel, it closes the contacts that connect the battery and starter and then the engine is cranked.
As soon as the engine starts, the flywheel ring gear begins turning fast enough to drive the pinion at an extremely high rate of speed. At this point, the one-way clutch begins allowing the pinion to spin faster than the starter shaft so that the starter will not operate at excessive speed. When the ignition switch is released from the starter position, the solenoid is de-energized, and a spring contained within the solenoid assembly pulls the gear out of mesh and interrupts the current flow to the starter.
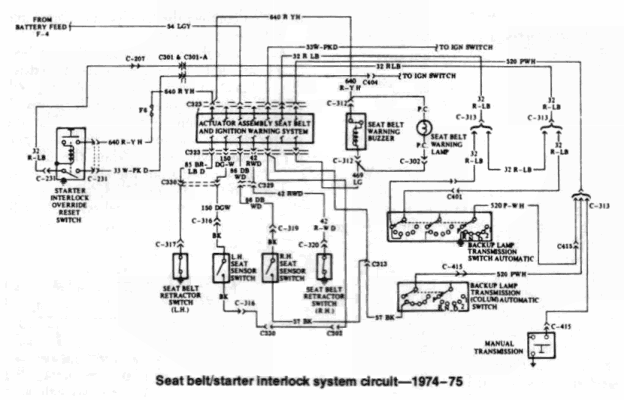
SEAT BELT/STARTER INTERLOCK SYSTEM—1974-75
On all 1974 and some early 1975 models, a starter interlock system is employed consisting of a warning light buzzer, seat sensors, switches in the outboard belt retractors, and an electronic logic module. Basically, the starter will not engage unless the driver and other front seat passenger sit in the seat and pull out the seat belt. Unless the driver or passenger has remained seated and buckled, the sequence must be repeated every time the engine is started. Leaving the belts pulled all the way out also will prevent the engine from being started, as the belts must be retracted and buckled each time the engine is started. In the event of a starter interlock system failure, or to permit the use of a remote starter switch when working under the hood, a starter interlock by-pass switch is located in the engine compartment on the left wheel well, thereby eliminating the need to perform the buckling sequence. NOTE: Each time the by-pass switch is operated, the buckling sequence may be eliminated once and once only. The system may not be permanently by-passed using the switch.
STARTER
Removal And Installation
- On models equipped with a 302 V8, raise the front of the car and position jack stands beneath the car at the front jacking points.
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Disconnect the starter cable at the starter terminal.
- Remove the 3 starter mounting bolts and withdraw the starter.
NOTE: It may be necessary to turn the front wheels to one side so that the starter clears the steering linkage. - To install, position the starter assembly to the flywheel housing and screw the mounting bolts in by hand.
- Snug the bolts while holding the starter squarely against its mounting surface, making sure that it is fully inserted into its pilot hole. Torque the mounting bolts to 15-20 ft. lbs.
- Connect the starter cable. If raised, lower the vehicle. Connect the negative battery cable.
Starter Drive Replacement
- Remove the starter from the engine.
- Remove the brush cover band.
- Remove the starter drive plunger lever cover.
- Loosen the thru-bolts just enough to allow removal of the drive end housing and the starter drive plunger lever return spring.
- Remove the pivot pin which attaches the starter drive plunger lever to the starter frame and remove the lever.
- Remove the stop ring retainer and stop-ring from the armature shaft.
- Remove the starter drive from the armature shaft.
- Inspect the teeth on the starter drive. If they are excessively worn, inspect the teeth on the ring gear of the flywheel. If the teeth on the flywheel are excessively worn, the flywheel should be replaced.
- Apply a thin coat of white grease to the armature shaft, in the area in which the starter drive operates.
- Install the starter drive on the armature shaft and install a new stop-ring.
- Position the starter drive plunger lever on the starter frame and install the pivot pin. Make sure the plunger lever is properly engaged with the starter drive.
- Install a new stop ring retainer on the armature shaft.
- Fill the drive end housing bearing fore Vi full with grease.
- Position the starter drive plunger lever return spring and the drive end housing to the starter frame.
- Tighten the starter thru-bolts to 33-75 in. lbs.
- Install the starter drive plunger lever cover and the brush cover band on the starter.
- Install the starter.
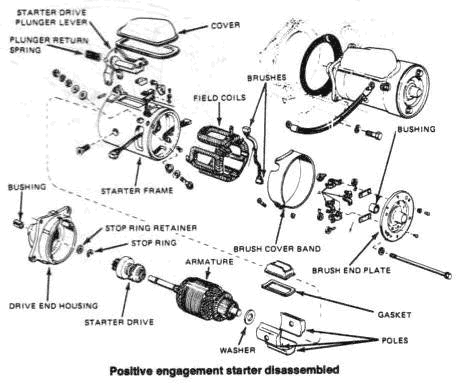
Starter Ground Brush Replacement
- Remove the starter from the engine.
- Remove the brush cover band and starter drive gear actuating lever cover. Observe the brush lead locations for reassembly, then remove the brushes from their holders.
- Measure the brush length. The factory wear limit is 1/4 inch.
- Remove the screws holding the brushes to the frame.
- Replace the brushes.
- Replace the brush cover band and starter drive gear actuating lever cover.
- Replace the starter.NOTE: It is far easier to replace the brushes while the starter is disassembled. If you are replacing the starter drive, always check the brushes for wear.
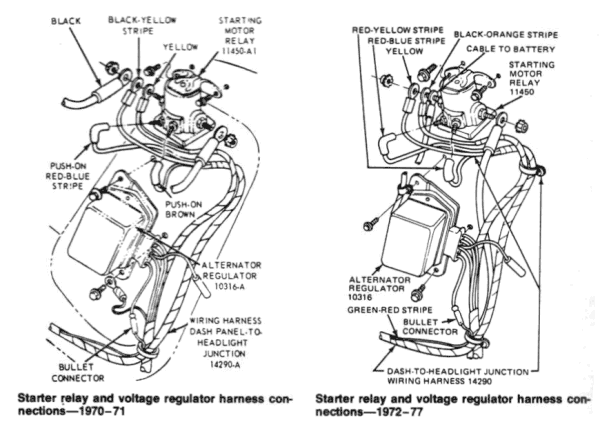
Starter Relay Replacement
Ford starter relays are mounted on the fender well near the battery. In the event the relay goes bad, replacement is simple. Disconnect the negative battery cable. Disconnect the positive battery cable and any wires from the relay, noting their position. Unbolt the relay from the fender well and replace. Replace the wires and the battery cable.
Battery
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
- Loosen the battery cable bolts and spread the ends of the battery cable terminals.
- Disconnect the negative battery cable first.
- Disconnect the positive battery cable.
- Remove the battery hold-down.
- Wearing heavy gloves, remove the battery from under the hood. Be careful not to tip the battery and spill acid on yourself or the car during removal.
- To install, wearing heavy gloves, place the battery in its holder under the hood. Use care to avoid spilling the acid.
- Install the battery hold-down.
- Install the positive battery cable first.
- Install the negative battery cable.
- Apply a light coating of grease to the cable ends.